Last year I had the pleasure of visiting Ireland, land of my ancestors. While there, I specifically visited a number of sacred places, looking to immerse myself in the land’s rich history of spirituality. The one I was most looking forward to visiting was Brigid’s Well outside Kildare.
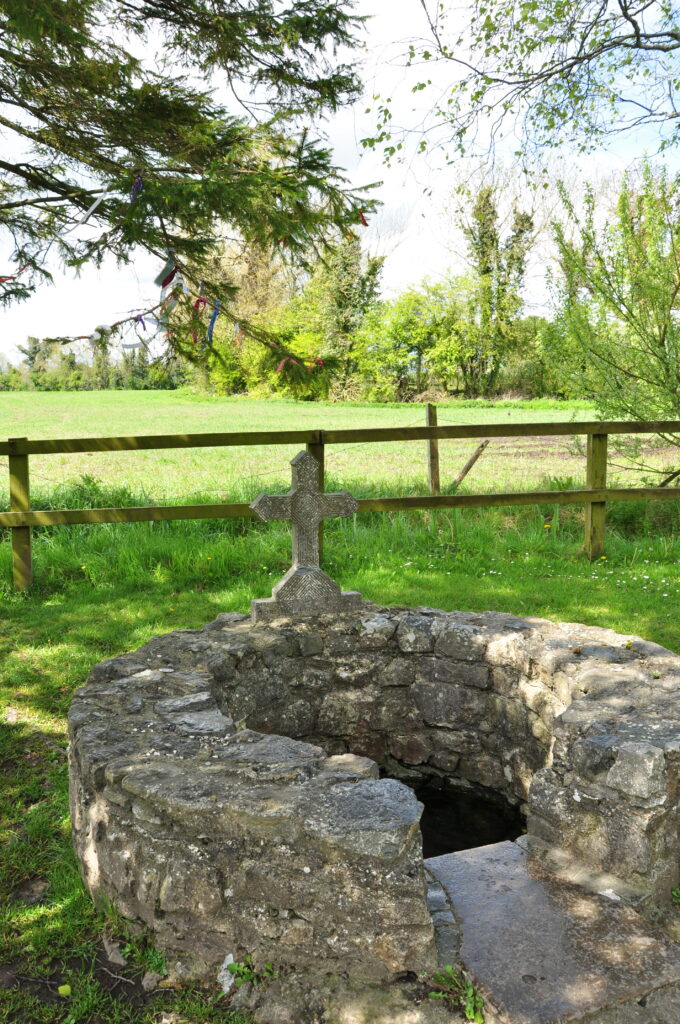

There are a number of wells all over Ireland linked to St. Brigid of early Irish Christian history. Although the Saint likely never lived, she was associated with agriculture, especially cows. Her feast day is on February 1; this same day is also known as Imbolc and was originally associated with the Celtic fire goddess Brigid. Archeologists indicate that some of the wells dedicated to St. Brigid are Celtic in origin and were once sites of fertility rites or other kinds of pagan rituals. After doing my research, I chose to visit the one located outside of Kildare because it wasn’t as famous as other wells, and there is a local group – the Brigidine Order — who still tend Her flame.
Sacred wells are rarely human artifacts, but may have structural elements added to them (likely to provide better access to the well). Originally sacred to the earth goddess, many have been Christianized by the Catholic Church by associating them with female saints. “The term ‘holy well’ is commonly used to refer to any water source of limited size (i.e. not a lake or river, but including pools and natural springs and seeps), which has some significance in the folklore of the area where it is located, whether in the form of a particular name, an associated legend, the attribution of healing qualities to the water through the numinous presence of its guardian spirit or Christian saint, or a ceremony or ritual centered on the well site. ” It has been said that all wells are sacred to the Goddess, as they are doorways to the Underworld and the womb of the Earth. People have visited these sacred wells for healing and divination, utilizing the emergence of living water as a tangible symbol of generation and purification. Interestingly enough, Christians [or Catholics?] visit these wells for the same purpose despite the co-option that has occurred. Often they don’t even hide the original infrastructure around a well, they expand upon what already exists; the contrast can be striking.
Out from town, down a road, turning into a lane, I knew only that I was in the middle of Ireland’s famous horse country. Tall hedges concealed stone walls that had been laid there 100s of years before, and just when I thought I might be lost, the lane ended at a small cull de sac. A brightly babbling brook flowed between the car park and the small park that contains Her well. Someone had been doing some gardening: bright flowers bloomed on either side of the wooden bridge over the brook, lovingly weeded. A tall stone column with a hollowed opening stands just inside and to the left. It is a fairly modern construction, and mostly dedicated to the Catholic Mary, with votive offerings, plastic flowers, and worn pictures sheltering inside the hollow. It feels remarkably like an altar. A sign nearby reads “Tobar Bríde: say the rosary at the station stones.”
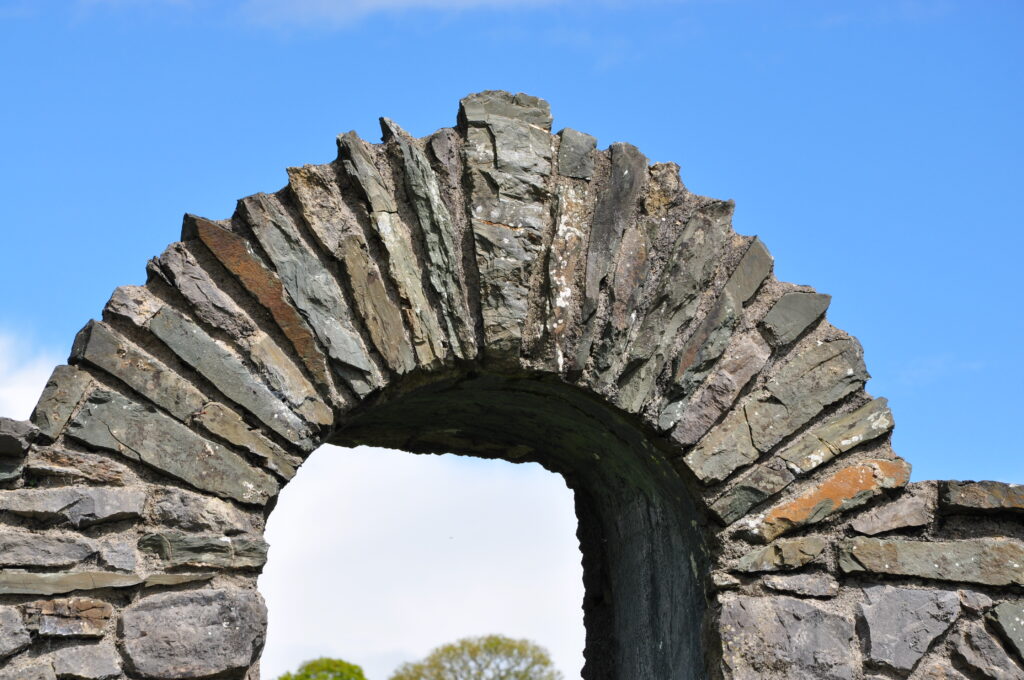

A modern well, complete with a life-sized bronze statue of Brigid is to the right, across the brook which flows from a well covered by a stone arch. Her cross is carved into the capstone, and painted white to strongly contrast with the dark stone. Water flows from two ‘shoes’ which some have likened to breasts. The use of brick and hewn stone reveals its comparatively young age, as does the statue. St. Brigid holds a crosier, wears a cross, and holds a flame in her hand – once again, a mingling of her ancient lineage and her Christian reinterpretation. In the center of the park, a series of stones, five in all, follow the path of the underground steam and lead you to the original well, enclosed and protected by stone. An equal-armed stone cross sits above it – more closely resembling the astrological sign for earth than the Christian cross.
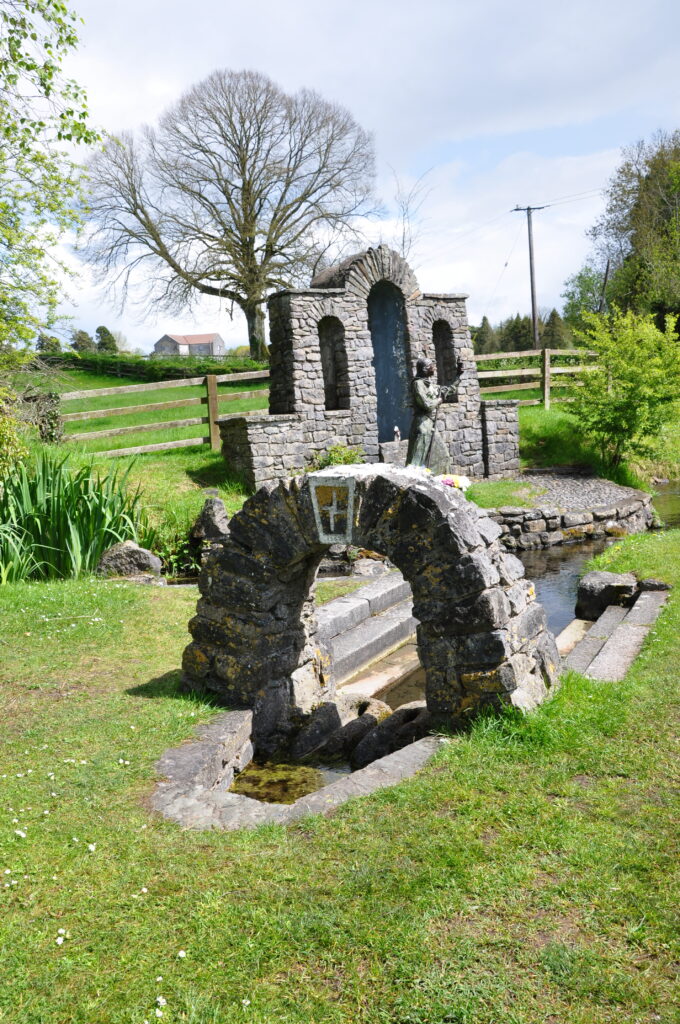

Behind the well, several trees were covered with ‘clootie rags’ – strips of cloth, some braided or curled, and fetish objects, all clearly part of some ritual observance. (The name “clootie” comes from the word for cloth.) One tree was nearly covered in the rags, some brightly colored, others faded by time. I’d never heard of this practice before I went to Ireland, and when I asked a local about it, I was charmed by the answer.
“Oh yes, that’s an old tradition. You take a bit o’ cloth – it has to be good cloth, something natural, something you love – and you dip it in the well, and then tie it to a tree. But not just any tree! No, it’s got to be a whitethorn [hawthorne], or maybe an ash tree. If your spirit is true, Brigid’ll take your pain away.“
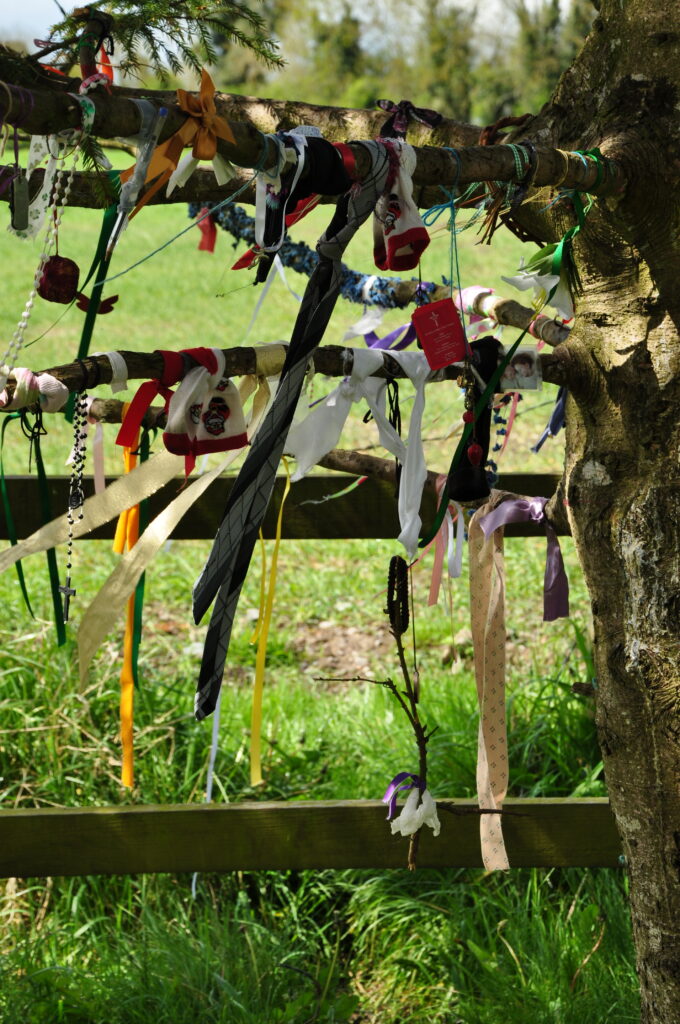

(Note: As I said in my last post — this is a fine custom for locals. You, as a visitor do not have the right to engage in their rituals . . . and the genus locii don’t want you to. Pick up any trash as an offering, if you must leave one.)
The hawthorn tree (sceach gheal in Irish) plays an important role in Celtic mythology. Thomas the Rhymer met the Fairie Queen by one, and of course there is the famous tree planted on Glastonbury Tor by Joseph of Arimetha (uncle of Virgin Mary). Legends and lore tell us that the fey often make their homes in hawthorn trees, and more than one field we passed had a wide swath of grass untouched around a lone tree in its center. It is tremendous to realize that this practice – one clearly from pre-Christian times – continues to this day.
There are several benches here, inviting one to sit and be still, enjoying the fresh air, the sounds of birds, and the slight scent of flowers and grass. In a blatant melding of old and new, one is invited to pray the Five Virtues of Brigid at each of the standing stones while walking round them clockwise seven times. The virtues vary a bit, but the ones I resonated best with are:
Stone #1: Brigid of the land.
Stone #2: Brigid as Peacemaker.
Stone #3: Brigid as Hearth-keeper, she who keeps the fire lit.
Stone #4: Brigid as Healer.
Stone #5: Brigid as Contemplative.
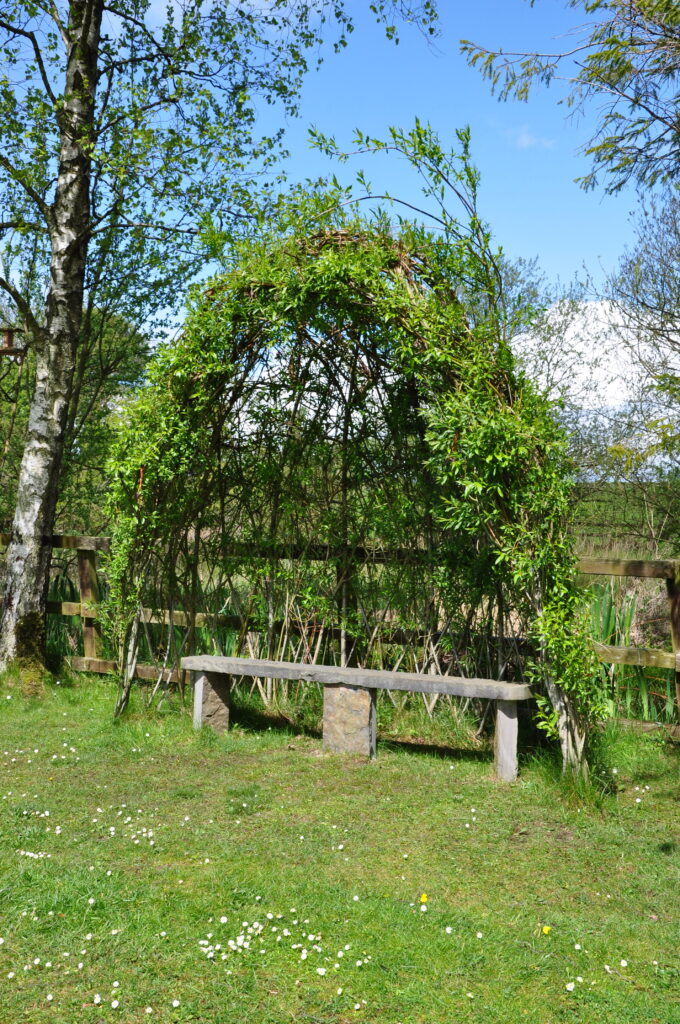

Brigid’s Well is a place of great peace. In a land with a living history, where poets and druids both turn to their connection with the land to express their spirituality, it is awe-inspiring to stand in a place sacred to the Goddess which is still actively used. When I reached down, a bit precariously, to drink from the well, I realized that I had joined a long line of my ancestors. We all had dipped into the same waters; we all whispered our supplications, our prayers, our gratitude. Like those before me, I left the Brigid’s Well renewed by the power of the land.
There are many sacred wells in Ireland, here is a list (by county) to get you started on your own sacred tour.
Clare
St. Brigid’s Well – Liscannor
Magh Adhair – Quin
Eye Well – Burren
Tooth Well – Burren
Margaret’s Well – Ennis
St. Augustine’s Well – Kilshanny
Cork
St. Olan’s Well – Aghbullogue
Tobrid Well – Millstreet
Ballinspittle
Inchigeela
Sunday’s Well and Mary’s Well – Walshestown
St. Finbar’s Well, Gougane Barra
Kerry
Well of the Wethers – Ardfert
St. Dahlin’s – Ballyheige
St. John’s Well – Dingle
St. Erc’s Well – Listowel
St. Eoin’s Well – Listowel
St. Michael’s Well – Ballymore West
Lady Well – Ballyheige
Kildare
Earl’s Well – Kildare
St. Brigid’s Well – Kildare
Father Moore’s Well – Kildare
Meath
Tobar Patraic – Ardmulchan
St. John’s Well – Warrenstown
Tara (Neamnach, Toberfin, and Leacht) – Castlebye
Roscommon
Tober Oglalla – Tulsk
St. Lassair’s Well – Lough Meelagh
St. Attracta’s Well – Monasteraden
Sligo
Tobernault – Sligo
St. Brigid’s Well – Cliffony
Tullaghan Well – Tullaghan
St. Patrick’s Well – Dromard
St. Patrick’s Well – Aughris
The Bog – The Culleens